In the broader conversation of programming languages, it’s easy to think that JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is the best data serialization format. It’s widely known and an ideal format for securely transmitting structured data.
But the JSON vs. YAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language) debate is a bit more complicated. JSON’s popularity is an advantage, yet YAML may be a better fit depending on several factors (like data type and whether you need a format for data storage as well as data transfers).
Which one is best for you will depend on what you’re using it for and who’s using the data serialization format.
What is JSON?
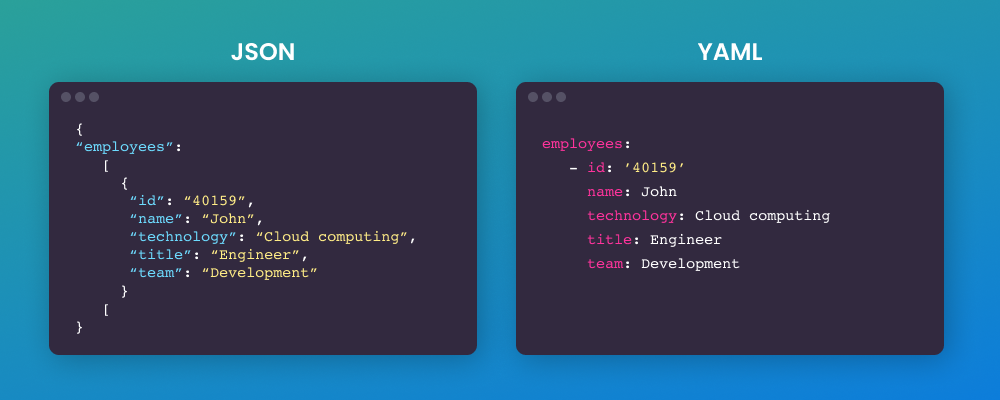
JSON is a lightweight data-interchange format for data exchange between different systems. Because it’s a text-based format that uses JavaScript syntax, JSON is fairly easy for humans to read and write, but it’s also easy for machines to parse and generate.
This data serialization format was developed around the same time as YAML. It was first developed in 2001 and took off as a lighter format than XML (Extensible Markup Language), which is an older data format used for storing or transferring data.
JSON is widely seen as the industry standard. It continues to be the most widely used format for data transfers. But it doesn’t work for every situation. JSON is primarily used for serializing and transmitting structured data over a network connection, not data in storage.
It’s a secure data format used for handling numbers, strings, objects, and arrays. If you need to handle other data types (like nested values or timestamps), you’ll need to look to another data format.
What is YAML?
YAML is the most human-readable data serialization format. Many developers consider it easier to learn than JSON because it’s written using natural language. In fact, YAML is a superset of JSON. It was developed around the same time to handle more kinds of data and offer a more complex but still readable syntax.
Developers often liken YAML to Python because the syntax is so similar. If your team is already familiar with Python, YAML might be the right fit.
Like JSON, YAML is used for configuration files and applications where data is being transferred. It can also be used for data that’s being stored — it’s a more versatile format than JSON. Additionally, YAML was made to handle a larger variety of data types than JSON. In addition to things like numbers and strings, YAML can handle dates, timestamps, sequences, nested values, null values, and Boolean.
There’s plenty YAML can do that JSON just can’t. But there are also situations where JSON outshines YAML (like in data security), so what’s best for each situation will vary.
JSON vs. YAML: which do I use?
When choosing which data format to use, you’ll need to consider who will be using it and for what. Your team’s history with syntax and data will play into which format is right for your team. Has the team already learned JavaScript syntax? If so, adopting JSON would be that much easier. But if you need a data format for handling integers, YAML is the way to go.
Learn more about these JSON vs. YAML use cases below so you can pick the best data serialization format for your needs.
JSON use cases
JSON is widely regarded as the gold standard in data formats. It may be a good fit for you and your team if you’re looking for a data serialization format that’s:
- Easy to learn and adopt — For developers already familiar with JavaScript, JSON is quick to learn because it uses the same syntax. Meanwhile, YAML requires learning a new syntax and can be more complex since it applies to more situations and data types. Many developers are also already familiar with JSON, so the transition to the format is smooth for many teams.
- Fast and easy to validate — YAML tends to be fussier about small errors. Because YAML uses space to represent structure, a single extra line break or an extra click of the space bar can throw a wrench in your code.
- Compact — JSON is more compact than YAML, too, making JSON faster to parse than YAML. This is another reason many developers prefer JSON.
- Secure — JSON is more secure than YAML. It’s less prone to security vulnerabilities, and in an age when security breaches are common, that’s a big plus.
- Able to connect with other systems — JSON is more suitable for data interchange between systems than YAML. So, for those who need a popular, lightweight data serialization format ideal for moving data from one place to another, JSON will probably be the right option.
- API data exchange — JSON is widely used in APIs to format the data being exchanged between a client (like a web or mobile app) and a server. It’s lightweight, easy to read, and natively supported by JavaScript, making it ideal for web development.
YAML use cases
While JSON has a lot of advantages, YAML comes with some tricks up its sleeve too. It may be a good fit for you and your team if you’re looking for a data serialization format that:
- Handles a variety of tasks — YAML can handle more tasks than JSON. It’s ideal if you’re working with multiple data types, want to leave comments, and/or need a format for storing as well as transferring data.
- Works with multiple data types — YAML supports data types like integers and floats, while JSON doesn’t. YAML also supports more complex data structures like lists and associative arrays too, which JSON can’t handle.
- Allows comments — YAML supports comments, which are not supported at all in JSON.
- Uses natural language — YAML is written in natural data format, making it quick and easy for beginners to learn the syntax.
- API configuration — YAML is often used in APIs, particularly for configuration files. For example, YAML files might define the settings for API endpoints, authentication methods, or data schemas.
If you need your data format to tackle nearly every situation and data type you throw at it, YAML is the answer.
The verdict: JSON and YAML are both useful
The choice between JSON and YAML largely depends on your specific needs and the context in which these formats will be used. JSON is ideal for scenarios where ease of use, security, and data interchange between systems are priorities, especially in environments familiar with JavaScript. It’s the go-to for many developers due to its simplicity and widespread adoption in APIs.
On the other hand, YAML shines in its versatility, human readability, and ability to handle more complex data types, making it a better fit for configuration files and scenarios that require managing a variety of data structures.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by your team’s expertise, the nature of your projects, and the particular requirements of your data workflows.

How SnapLogic supports JSON and YAML
At SnapLogic, we understand that both are valuable and needed formats for handling data in different scenarios.
SnapLogic is an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) that helps organizations automate and streamline data integration, application integration, and API management. It provides tools and features that simplify working with data in various formats, including JSON and YAML.
Here are the various ways SnapLogic assists with these formats:
Data integration and transformation
- JSON handling: SnapLogic offers built-in capabilities to parse, generate, and manipulate JSON data within its integration pipelines. This makes it easy to work with JSON data when integrating different applications, databases, and services.
- YAML support: While JSON is more commonly used in data exchange, YAML is often used for configuration files. SnapLogic supports handling YAML data, allowing users to manage configurations, process YAML files, and convert between YAML and other formats as needed.
API management and integration
- JSON in APIs: SnapLogic’s API management features enable the creation, deployment, and management of APIs that often rely on JSON for data exchange. SnapLogic allows users to define API endpoints that accept and return JSON data, facilitating integration with web services and applications.
- YAML for API configurations: SnapLogic can leverage YAML for defining API specifications, such as those outlined in OpenAPI (formerly Swagger). YAML’s readability and structure make it a good choice for configuring and documenting APIs, which can then be integrated and managed within SnapLogic.
Data transformation and mapping
- JSON transformation: SnapLogic provides tools for transforming JSON data, including mapping fields, converting data types, and applying business logic. This is particularly useful when integrating systems that use different data formats or when preparing data for analytics.
- Format conversion: SnapLogic allows conversion between JSON and YAML formats, helping users adapt data and configurations to the specific needs of their environment. This flexibility is crucial when working with diverse systems and data sources.
Pre-built connectors and snaps
- SnapLogic offers a variety of pre-built connectors, known as “Snaps,” that facilitate working with JSON and YAML data. These Snaps can be used to connect to REST APIs, parse JSON or YAML files, and integrate data across cloud services, databases, and enterprise applications.
Ease of use and automation
- SnapLogic’s drag-and-drop interface simplifies the process of working with JSON and YAML, making it accessible even to those who may not have extensive coding experience. This ease of use, combined with automation features, helps organizations efficiently manage data workflows involving these formats.
SnapLogic provides comprehensive support for JSON and YAML through its integration, transformation, and API management capabilities, enabling businesses to streamline their data processes and improve interoperability across systems.
No matter which format is right for your project, SnapLogic can handle it. Request a free demo to learn more about what you can do with your data.