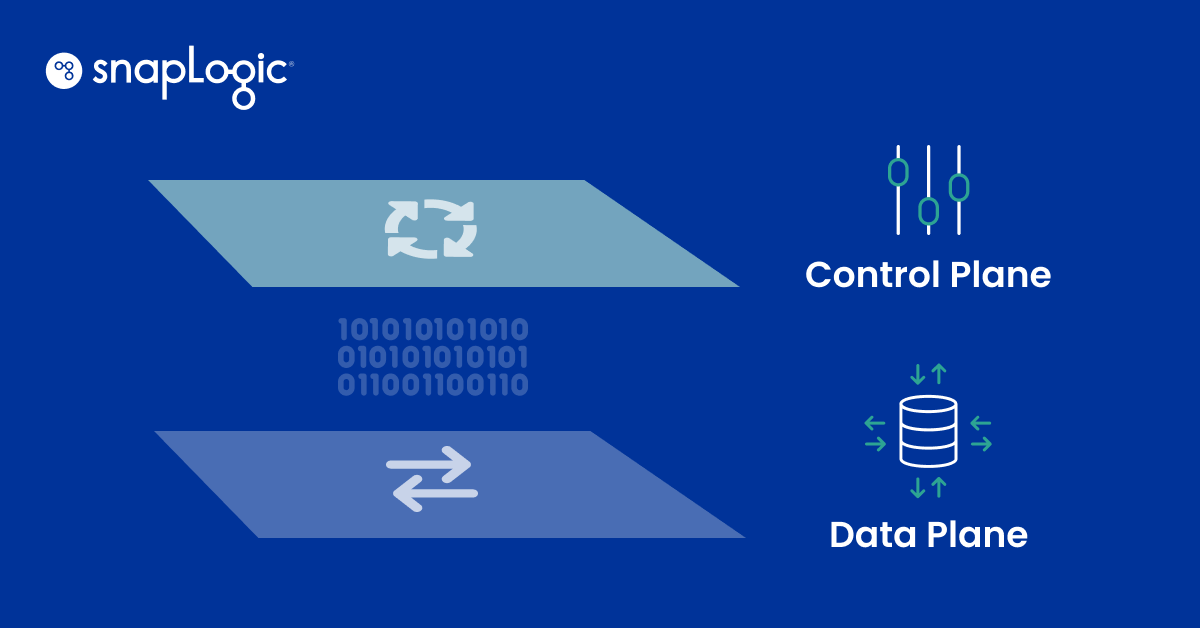
In the realm of network management, two key components play a pivotal role in how data is handled – the control plane and the data plane. These two entities, while working in tandem, perform distinct functions that are integral to the smooth operation of a network. This article delves into the roles of the control plane and data plane, their differences, and their impact on an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) environment.
What is a control plane?
The control plane is a crucial network component, making decisions on how data should be managed, routed, and processed. It acts as a supervisor of data, coordinating communication between different components and collecting data from the data plane.
Control planes utilize various protocols, such as:
- Routing protocols (like BGP, OSPF, and IS-IS)
- Network management protocols (SNMP)
- Application layer protocols (HTTP and FTP)
These protocols often employ software-defined networking (SDN) to create virtual networks and manage their traffic. Virtual networks, facilitated by SDN, are instrumental in managing data traffic at an enterprise level. They enable organizations to:
- Segment traffic
- Prioritize important data flows
- Isolate traffic from different parts of the network
What is a data plane?
While the control plane supervises and directs, the data plane is responsible for the actual movement of data from one system to another. It is the workhorse that delivers data to end users from systems and vice versa.
Some examples of data planes include:
- Ethernet networks
- Wi-Fi networks
- Cellular networks
- Satellite communications
Data planes can also include virtualized networks, like those created using virtual private networks (VPNs) or software-defined networks (SDNs). Additionally, data planes can include dedicated networks, like the Internet of Things (IoT) or industrial control systems.
Data planes allow organizations to quickly and securely transfer data between systems. For example, a data plane can enable the transfer of data between a cloud-based application and a local system. This functionality can be beneficial for organizations that need to access data from multiple systems or that need to quickly transfer large amounts of data.
By using dedicated networks, organizations can keep data secure through encryption, dedicated networks, and access monitoring to prevent unauthorized access of data.
Data plane vs. control plane: what are the key differences?
The main differences between control and data planes are their purpose and how they communicate between different systems. The control plane decides how data is managed, routed, and processed, while the data plane is responsible for the actual moving of data. For example, the control plane decides how packets should be routed, and the data plane carries out those instructions by forwarding the packets.
Along with doing different jobs, control planes and data planes exist in different areas. While the control plane runs in the cloud, the data plane runs in the data processing area.
They also use different functions to do their jobs. Control planes use protocols to communicate between different systems, mostly common routing protocols like BGP, OSPF, and IS-IS or network management protocols like SNMP. These protocols enable the control plane to make decisions on how data should be managed, routed, and processed.
Data planes use dedicated networks to communicate between different systems. Examples of dedicated networks used in data planes include Ethernet and Wi-Fi networks, cellular networks, satellite communications, virtualized networks, and dedicated networks used in industrial control systems or IoT. These networks enable the data plane to deliver data to end users from systems and vice versa.
While both the control plane and data plane are integral to network management, they perform distinct roles. The table below outlines some of the key differences between the two:
| Control Plane | Data Plane |
|---|---|
Determines how data should be managed, routed, and processed | Responsible for moving packets from source to destination |
Builds and maintains the IP routing table | Forwards actual IP packets based on the control plane’s logic |
Packets are processed by the router to update the routing table | Forwards packets based on the built logic of the control plane |
How do control planes and data planes work with an iPaaS?
An iPaaS is a platform that connects disparate systems — collecting and analyzing data in real time and then publishing that data to different applications. Control and data planes are essential components of an iPaaS environment, directing and managing the flow of data.
By using an iPaaS, organizations can create secure networks using data planes to protect data. iPaaS can also be used to monitor and analyze data traffic, providing organizations with the insights they need to improve control plane functionality and make informed decisions about their data pipeline.
An iPaaS can also enable organizations to segment data traffic, prioritize important data flows, and isolate traffic from different parts of the network — all important for control and data plane effectiveness. Additionally, an iPaaS can help organizations maintain the security of their data pipeline by preventing unauthorized access and encrypting data in transit.
Organizations can also use an iPaaS to quickly and securely transfer data between systems. For example, an iPaaS can enable the transfer of data between a cloud-based application and a local system. This can be beneficial for organizations that need to access data from multiple systems or that need to quickly transfer large amounts of data.
By using an iPaaS, organizations can keep data secure and always accessible.

Choosing an iPaaS
When selecting an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) platform, companies should carefully evaluate several critical considerations to ensure the solution aligns with their business needs and technical requirements.
Here are some key factors to consider:
Integration capabilities
- Support for various data sources and applications: Ensure the iPaaS can connect to all the necessary data sources, applications, and systems, including legacy, cloud-based, and on-premises solutions.
- Data transformation: look for robust data transformation tools that can handle complex mappings, enrichments, and data conversions
- API management: check for comprehensive API management capabilities, including the ability to create, manage, and monitor APIs.
Scalability
- Elasticity: The platform should scale up or down based on demand, supporting varying workloads without performance degradation
- Support for high volumes: Ensure it can handle high data volumes and transactions, especially if your business expects growth.
Ease of use
- User-friendly interface: The platform should offer an intuitive, low-code/no-code interface that enables business users to create and manage integrations without deep technical expertise
- Pre-built connectors: (Snaps, in the case of SnapLogic) for common applications and services can significantly reduce development time.
Performance and reliability
- Latency: Evaluate performance in terms of data processing speed and real-time capabilities
- Uptime: check the platform’s reliability, including its history of uptime and availability guarantees.
Compliance and security
- Data encryption: ensure the platform offers robust security measures, including end-to-end encryption of data in transit and at rest
- Compliance: the platform should support compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2) specific to your industry
Cost
- Pricing model: understand the pricing structure (e.g., subscription-based, pay-per-use) and evaluate it against your budget and projected usage
- Hidden costs: be aware of potential hidden or compounding costs, such as those for additional data transfer volumes
Vendor support and community
- Customer support: evaluate the quality and responsiveness of vendor support, including the availability of dedicated support teams or SLAs
- Community and ecosystem: a strong user community and ecosystem can provide valuable resources, best practices, and third-party integrations
Monitoring and analytics
- Real-time monitoring: the platform should offer comprehensive monitoring tools to track the performance and health of integrations
- Reporting and analytics: look for robust reporting and analytics capabilities to gain insights into data flows and integration success rates
Vendor reputation and longevity
- Market position: consider the vendor’s position in the market, their track record, and their commitment to innovation, including GenAI applications
- Roadmap and future development: ensure the vendor has a clear roadmap for future development that aligns with your company’s long-term goals
Choosing the right iPaaS involves balancing these factors based on your specific business needs, existing technology stack, and strategic objectives.
SnapLogic’s integration solution
SnapLogic’s AI-enhanced agentic integration platform supports cloud-based and on-premises deployments, for data or application integrations. All integrations are seamlessly managed through a cloud-native control plane called the Snaplex, which has a modern, graphical-browser user interface.
The Snaplex is a scalable data processing engine that executes the data integration pipelines created on the SnapLogic platform. It is essentially the runtime environment where the actual data movement, transformation, and integration processes occur.
Key features and components of the Snaplex:
- Elasticity: scales up or down based on demand, making it adaptable to varying workloads
- Multi-cloud and on-premise: can be deployed in the cloud (on major platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud) or on-premises, depending on the organization’s requirements
- Data flow management: manages data flows between different sources and destinations, handling tasks like data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL), API integrations, and more
- High availability: designed for high availability, with the ability to automatically failover and distribute workloads across multiple nodes to ensure continuous operation
- Security: supports encryption and other security features to ensure data privacy and compliance with various regulatory standards
- Monitoring and management: SnapLogic provides tools to monitor and manage Snaplex instances, allowing users to track performance, diagnose issues, and optimize operations
The Snaplex is a critical component of the SnapLogic Integration Platform, enabling seamless and efficient data and application integration across different environments.
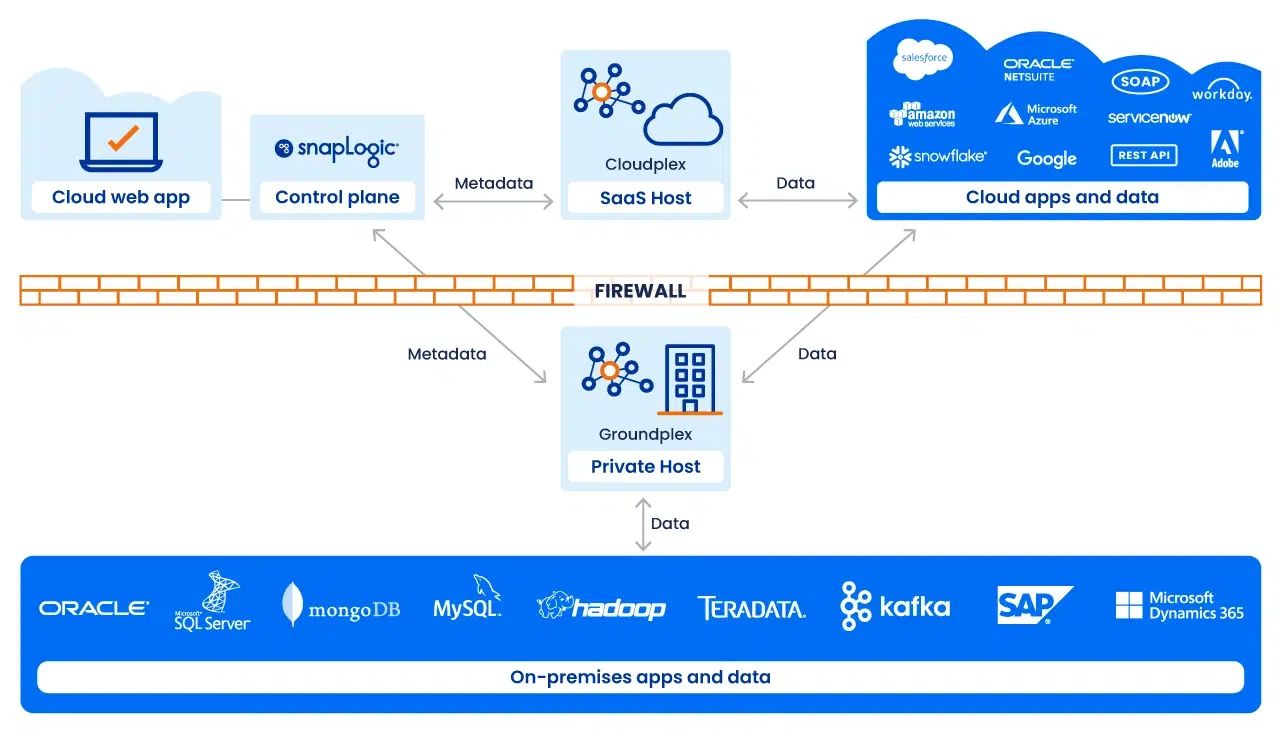
The importance of control planes and data planes in iPaaS network management
Understanding the distinct roles of the control plane and data plane is essential for effective network management, especially within an iPaaS environment. While the control plane is responsible for decision-making and traffic management, the data plane focuses on the actual movement of data across the network. Together, they form a cohesive system that supports seamless integration, data flow management, and security.
By leveraging both planes effectively within a modern iPaaS platform, organizations can ensure efficient, secure, and scalable data operations, empowering them to meet their integration needs in an increasingly complex digital landscape.